 In the rectangular form we can express a vector in terms of its rectangular coordinates, with the horizontal axis being its real axis and the vertical axis being its imaginary axis or j-component.
In the rectangular form we can express a vector in terms of its rectangular coordinates, with the horizontal axis being its real axis and the vertical axis being its imaginary axis or j-component.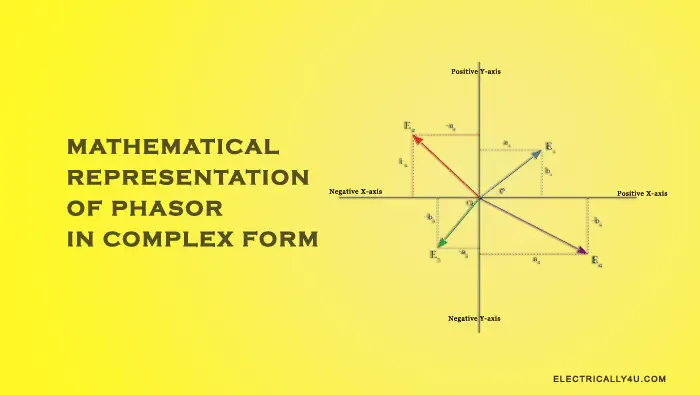 In rectangular form, the phasor quantities are algebraically expressed in terms of rectangular components. It is also called a Cartesian form of representation. In this form, a phasor can be divided into two components, namely a horizontal component and a vertical component.
In rectangular form, the phasor quantities are algebraically expressed in terms of rectangular components. It is also called a Cartesian form of representation. In this form, a phasor can be divided into two components, namely a horizontal component and a vertical component. The rectangular coordinates of a phasor consist of a real number (which can be positive or negative) and an imaginary number identified by either +j or –j. The real component is always listed before the imaginary component.
The rectangular coordinates of a phasor consist of a real number (which can be positive or negative) and an imaginary number identified by either +j or –j. The real component is always listed before the imaginary component.